
BIM-SPEED: Performing laser scanning and deviation analysis on Dutch demonstration case
BIM-SPEED: Performing laser scanning and deviation analysis on Dutch demonstration case
The 3D models of buildings form the basis of various BIM use cases. If the corresponding structures are existing buildings, the models are usually created on the basis of planning documents. Often, these planning documents are outdated, and subsequent renovation or conversion measures are unfortunately only added to the planning documents in the rarest of cases. It is difficult to ensure that the model corresponds to the existing building. Since the correctness of the model is a mandatory condition for many BIM use cases, it is important to ensure that the BIM model and the existing building are in harmony with each other.
In the context of Rule-based model checking and validation of data interoperability, a deviation analysis for the Dutch BIM-SPEED project demonstrator was performed. The goal of the analysis is to detect deviations between the 3D mesh of an architectural model and a point cloud and to adapt the model accordingly.
The procedure of such an analysis is as follows:
- First, the Revit model and the corresponding point cloud are imported into the editing software.
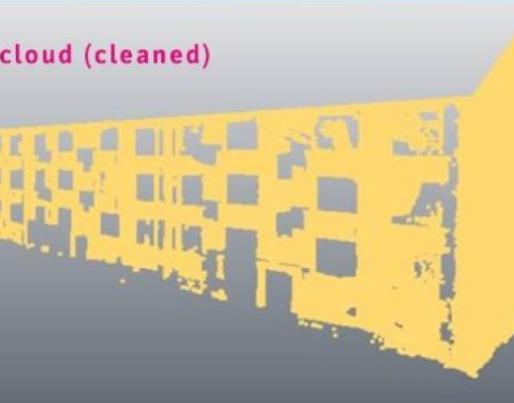
- If the point cloud was imported together with the model into the program, it is noticeable that the point cloud contains a large amount of point data. However, only a fraction of this point data is relevant to perform the deviation analysis, specifically, the point data related to the existing building is important. In order to obtain the best results, the irrelevant point data must be removed.
- To compare the point cloud with the model, it is necessary to extract a 3D mesh of the building shell from the model.
- Once the point cloud has been cleaned and the model has been converted into a 3D mesh of the building envelope, both objects can be aligned. For this step, an N Point Registration is used. The N Point Registration is a command of the editor software that allows the user to select a number of point pairs to superimpose (the 3D mesh is the starting point and the point cloud is the target point). Based on the selection of point pairs, the editing software calculates the transformation that minimizes the distance between each starting point and the corresponding target. Then it runs the Best Fit Registration command, which calculates the best possible fit between two objects. This command analyses the overlap of the selected objects to calculate the best of them. The best fit can be understood as the transformation that minimizes the distance to the other object in the least square way.
- If the point cloud and 3D mesh were successfully aligned, the results of the deviation analysis can be displayed by the processing software in the form of color schemes or other visualization options. However, the interpretation of the results is up to the user.
To know more about the BIM-SPEED demonstration cases.

