EERAdata Decision Support Tool: Practical Guide
EERAdata Decision Support Tool: Practical Guide
The EERAdata project has developed a Decision Support Tool for calculating the impact of building renovations on energy efficiency. In particular, it supports the decision-making during a renovation process. Find here the practical guide to use the tool.
The EERAdata project has developed a decision support tool (DST) for calculating the impact of building renovations on energy efficiency. This page provides a brief description of how the DST can be used to support decision-making in a typical renovation process and will provide a number of renovation cases where decisions will be made on whether the tool should be used or not.
The user journey through the DST is also described from data collection and input to data analysis and output for users on different levels of decision-making (standard and expert).
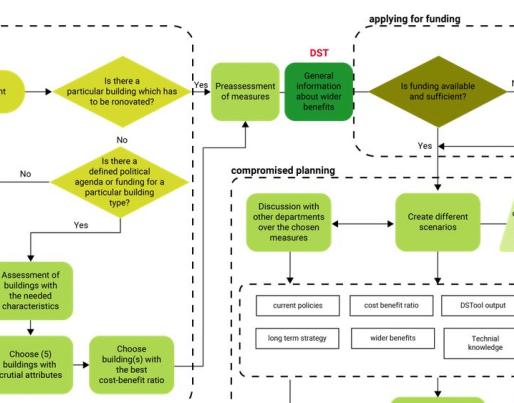
The DST can be applied in different contexts within a typical renovation process. As seen in figure 1 below, the DST can be useful in three distinct ways:
- To collect information and gather evidence on the wider benefits of the renovation process prior to applying for funding.
- To improve the planning process by extoling the benefits of the renovation packages contained within the tool itself.
- To provide the justification for increased investment by providing evidence of a reduced payback period and increased positive effects e.g., socioeconomic effects.
There are a number of different renovation strategies in which the decision to apply the DST can be analysed. These scenarios are typical renovation cases adapted from the partner municipalities of the EERAdata project and represent user stories which can occur for any building manager, owner, government department or municipality. They include strategies for an emergency renovation scenario, scheduled maintenance renovation scenario, long-term deep renovation scenario and a building renovation business case scenario.
- Emergency Renovation
- Scheduled Maintenance Renovation
- Long-term Deep Renovation
- Business Case: Building Renovation
The standard user can be described as one which does not have or require extensive technical knowledge and data to use the full functionality of the tool. As such, this user does not possess access to the entirety of the tool’s architecture. This user can be a building owner, or city planner. The standard user only has access to the Projects tab in the DST. This allows the user to be able to create a renovation project and add details to that project.
Within the projects tab, the standard user can add and edit building data, add the calculation units needed for the renovation project, and add renovation options to the project. It is important to note here that each building, once added to the project is copied into it, with all its properties and becomes independent of the general building stock stored in the application’s database. This means that calculations are made on the copies of the building properties and not on its actual parameters. The user can then conduct analysis by running the calculations to determine the impact of the proposed renovation action(s).
The expert user on the other hand, possesses and requires extensive technical knowledge to operate the different parts of the tool and understand more detailed outputs after analysis is conducted. This user can be a building manager, researcher, technical analyst in addition to being an owner or government level decision-maker. The expert user has access to the Projects, Buildings, Parameters, and Processing Tabs of the DST. This means that the user is able to add and edit building and projects data directly stored in the application’s database. The expert user can do this in two ways – by adding data directly and by uploading data through the prescribed data template.
Before data is added to the tool, it is important for it to first be cleaned and made ready for use in the DST. Data should be cleaned to sort out issues such as incorrect data types, data gaps, irrelevant, and duplicate data. This can be done based on the guidelines developed by the EERAdata project in D4.5. Following this, data can be added directly into the tool or can be uploaded through the prescribed data template which can be downloaded from the tool. Similar to the standard user, the expert user can then create a project, add buildings, add calculation units, add renovation options, and then conduct analysis by running calculations.
Find more information here.