
Geothermal grid powers buildings low-carbon future
Geothermal grid powers buildings low-carbon future
A pioneering Swedish project showcases how low-temperature geothermal networks and smart energy sharing between buildings can slash emissions, boost efficiency, and extend infrastructure lifespan—offering a pragmatic path to decarbonising urban heating.
Source: danfoss.com
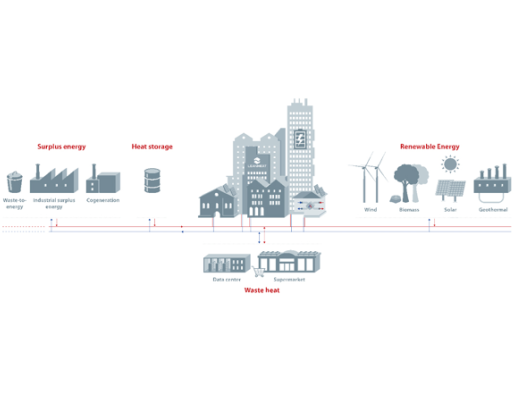
A study from Lund University explores a novel approach to reducing carbon emissions in the building sector through the use of low-temperature district heating and cooling networks. Centred around the Embassy of Sharing community in Malmö, Sweden, the project integrates shallow geothermal systems and smart energy-sharing technologies to meet the diverse heating and cooling needs of residential and commercial buildings.
At the heart of the system lies a network that allows buildings to exchange surplus energy, transforming them into both consumers and producers. This setup not only improves energy efficiency but also reduces waste, as excess heat from one building can be redirected to another in need. The system is managed through advanced control mechanisms and digital modelling, ensuring optimal performance and seamless coordination between substations.
The study found that energy sharing between buildings led to a 14% reduction in electricity use for heat pumps and significantly improved their seasonal performance. Moreover, the geothermal borefields benefited from balanced energy loads, extending their operational lifespan and enhancing long-term sustainability. These findings underscore the practical advantages of collaborative energy systems in urban environments.
Regarding the environmental impact, the low-temperature network produced just 7% of the emissions associated with Malmö’s conventional district heating system. This substantial reduction highlights the potential of such networks to play a pivotal role in Europe’s broader decarbonisation efforts. The study offers a scalable and replicable model for cities seeking to transition to cleaner, more efficient heating and cooling solutions.
Pragmatic design solution to decarbonize building industry through a low temperature district network.pdf
English (12.25 MB - PDF)